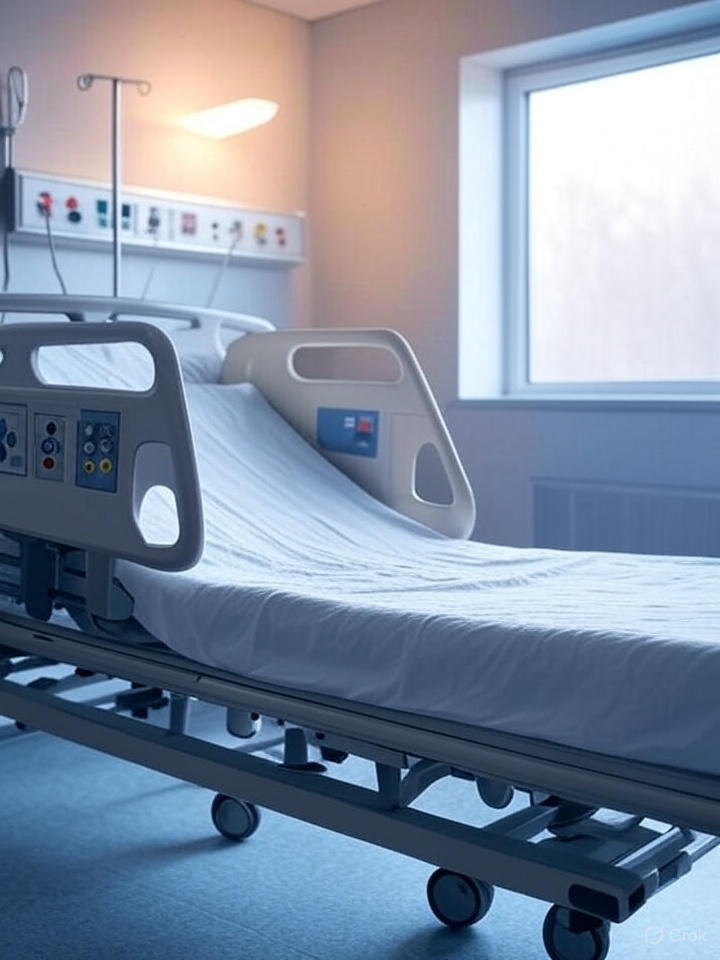
What Makes a Hospital ICU Bed Different? Key Features You Should Know
When it comes to critical care, every detail counts—especially the bed where a patient fights for life and recovery. A hospital ICU bed isn’t just a place to rest; it’s an integrated piece of medical technology that supports patient survival and clinician efficiency. In a high-pressure environment like the intensive care unit, these beds are designed with features that cater specifically to complex medical needs.
Before diving into what makes an ICU bed truly unique, it’s worth exploring other essential tools that help elevate care standards in a hospital, especially for young patients. Providers often rely on pediatrics medical supplies to ensure specialized comfort and care for children in ICUs and general wards alike. These tools are tailored not just to size, but to emotional and physical needs—making them a crucial part of pediatric healthcare delivery.
Now, let’s take a closer look at what exactly sets a hospital ICU bed apart, why it matters, and how its features influence patient outcomes.
Understanding the Purpose of a Hospital ICU Bed
Hospital ICU beds aren’t just glorified stretchers or regular hospital beds. Their design incorporates advanced functionalities required for critically ill patients, including cardiac monitoring, ventilator support, and frequent repositioning. ICU patients often experience immobility, respiratory complications, or neurological distress—all requiring a robust, responsive bed system.
Core Features That Differentiate a Hospital ICU Bed
1. Advanced Mobility & Positioning Control
A defining characteristic of any hospital ICU bed is its adjustability. ICU beds allow multi-directional positioning such as:
- Trendelenburg and reverse Trendelenburg
- Fowler’s position
- Cardiac chair configuration
These positions help manage respiratory conditions, promote circulation, and prevent pressure ulcers. Unlike basic beds, ICU beds feature motorized control systems allowing caregivers to change positions quickly and safely.
2. Integrated Monitoring Capabilities
Many ICU beds come with integrated systems that connect with patient monitoring devices. These features include weight sensors, oxygen saturation readers, and sometimes even ECG input ports. These integrations are crucial for real-time tracking and minimizing the need to move critically ill patients unnecessarily.
3. Enhanced Safety Mechanisms
ICU patients are often unconscious, heavily medicated, or mentally disoriented. Hospital ICU beds incorporate safety rails with easy-lock mechanisms, alarm systems that alert staff when patients attempt to move, and auto-regressive bed movement to reduce shear and friction injuries.
Material Quality and Infection Control Features
ICU settings require rigorous infection control. ICU beds are constructed with antimicrobial materials and are easy to sanitize. Surfaces are smooth, waterproof, and resistant to chemical disinfectants.
Further, the beds feature special mattresses—often low air loss or alternating pressure mattresses—to prevent bedsores and maintain skin integrity in immobile patients.
Electrical & Backup Power Systems
One important feature that sets a hospital ICU bed apart is its reliable electrical system. Beds operate on electronic motors with battery backups. During power outages, especially in under-resourced regions or during emergencies, these systems allow for uninterrupted patient care.
Specialized Pediatric ICU Beds
Pediatric ICUs (PICUs) require additional considerations. Hospital ICU beds designed for children incorporate side rails with adjustable heights, scaled-down dimensions, and integration for pediatric life-support systems. These beds, paired with pediatrics medical supplies, create a nurturing and safe environment even in the most critical situations.
Customization and Expandability
One size doesn’t fit all in the ICU. Beds must adapt to a range of patient sizes, weights, and medical needs. ICU beds feature modular components such as removable headboards, collapsible footrests, and ports for IV poles and oxygen tanks. These features provide clinicians with flexibility while improving access to the patient.
What Makes a Hospital ICU Bed Different in Functionality?
In the middle of a hospital’s critical care environment, ICU beds support more than just rest—they facilitate healing. Their features contribute to:
- Pressure injury prevention
- Pulmonary hygiene
- Safer nurse-patient interaction
- Timely detection of physical changes
These enhancements improve patient outcomes and optimize clinical workflows.
Cost Implications and Investment Value
Though expensive upfront, hospital ICU beds offer long-term value. They reduce the need for frequent replacements, lower the risks of hospital-acquired infections, and minimize complications through proper positioning and safety features.
Administrators often assess the ROI not just in terms of bed durability, but in patient recovery rates, hospital ratings, and care efficiency.
Technological Integration for Smart Healthcare
Some ICU beds are equipped with IoT (Internet of Things) capabilities, enabling communication with hospital systems. Smart beds can send alerts to nurses’ stations, monitor patient movement, and even collect data for analytics on treatment efficiency.
This next-gen evolution positions the hospital ICU bed as an active player in medical intervention—not just a passive fixture.
Conclusion: Why the Hospital ICU Bed is More Than Just a Bed
When lives hang in the balance, every feature becomes critical. From positioning controls and integrated monitors to safety mechanisms and infection-resistant materials, ICU beds embody innovation in modern healthcare. These beds aren’t mere pieces of hospital furniture—they are life-saving platforms engineered to meet the rigorous demands of intensive care units.
As hospitals advance, the role of a hospital ICU bed will continue to evolve—enhancing patient comfort, improving clinical outcomes, and ultimately saving more lives through thoughtful design and cutting-edge technology.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the basic types of hospital beds available?
The main types include manual beds, semi-electric beds, and fully electric beds. ICU beds fall under the fully electric category with added smart features.
How often should ICU beds be replaced?
Typically, ICU beds last 10–15 years. However, frequent use, weight loads, and technological obsolescence may shorten that span.
Can ICU beds be used in home care settings?
Yes, but only if the patient has intensive medical needs. These beds require proper setup and may need trained personnel for operation.
Are ICU beds covered by insurance?
In most countries, ICU beds used during inpatient hospital stays are covered under standard health insurance policies.
Do ICU beds help prevent bedsores?
Yes. ICU beds often come with specialized mattresses and movement features that significantly reduce the risk of pressure ulcers.
What is a Trendelenburg position, and why is it used?
This is a position where the patient lies flat on their back with legs elevated higher than the head. It helps in certain shock conditions and surgical situations.
Are pediatric ICU beds different from adult beds?
Yes. They are scaled for children, with appropriate safety features and often compatibility with pediatric medical equipment.
Can ICU beds monitor patient weight continuously?
Many high-end ICU beds feature built-in weight sensors that monitor changes without needing to move the patient.
How do nurses interact with ICU beds during emergencies?
ICU beds are designed for quick, smooth movement and easy access, which allows nurses to administer care swiftly during crises.
What is a low air loss mattress, and how does it work?
It’s a specialized mattress that circulates air to maintain skin integrity and minimize pressure, ideal for long-term ICU patients.